Solar Photovoltaic Mounting Systems: A Professional Analysis and Selection Guide
In photovoltaic power generation systems, while solar panels are the most visible component, the mounting system beneath them is crucial for ensuring safe and stable operation. PV mounting systems not only serve to secure the modules but also must adapt to different installation surface conditions and guarantee long-term reliability. This article provides an in-depth analysis of the composition, selection criteria, and characteristics of mainstream brands of PV mounting systems.
1. Function and Importance of PV Mounting Systems
A PV mounting system (also known as a PV mounting system) is a metal structure used to reliably fix PV modules to various surfaces (such as roofs or the ground). Its primary material is aluminum alloy, balancing strength and lightweight requirements, making it particularly suitable for scenarios with limited roof load capacity. Although mounting systems account for only about 3% of the total system cost (according to NREL data), they are a core factor affecting the system’s safety and durability.
2. Core Components of a PV Mounting System
A complete PV mounting system typically includes the following components:
Waterproof Flashings
Roof drilling installations require waterproof flashings to prevent leakage. These are typically made of aluminum sheeting and are embedded beneath asphalt shingles during installation. For specialized roofing materials like clay tiles, metal, or rubber, custom-designed flashings are necessary.
Support Mounts
Mounts are the load-bearing connectors between the system and the roof, securing the flashing to the roof rafters with bolts. A preliminary site assessment is required before installation to confirm the load-bearing capacity and spacing of the rafters meet installation requirements.
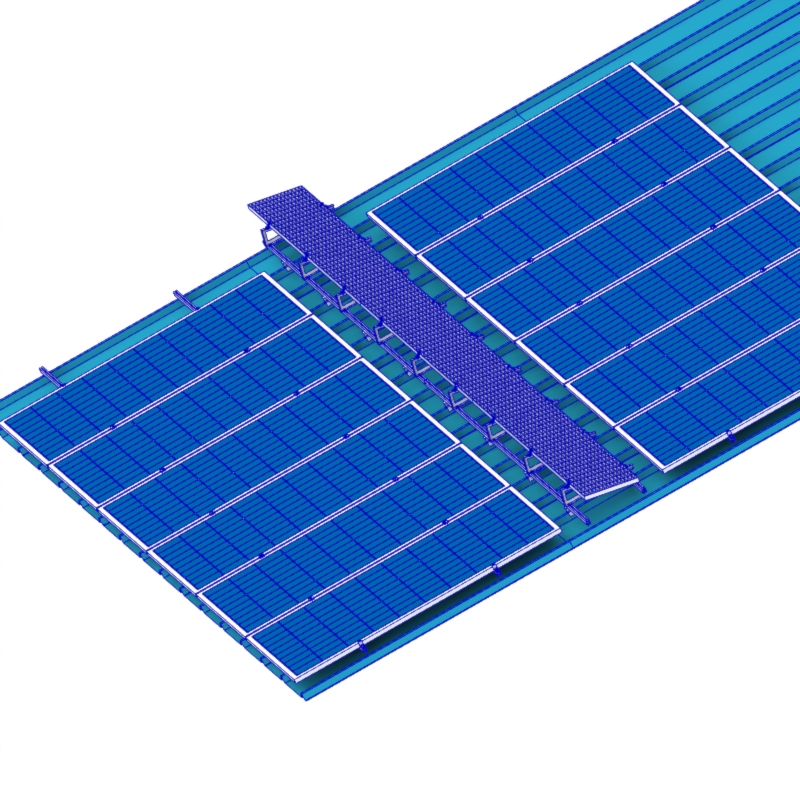
Rails
Serving as the load-bearing skeleton for the modules, rails are fixed vertically or horizontally to the roof via the mounts. Beyond their supportive function, they provide channels for cable management, optimizing system safety and aesthetics. In addition to conventional rail solutions, innovative designs like rail-less and shared-rail systems exist.
Clamps
Modules are secured to the rails using mid-clamps and end-clamps. Mid-clamps are used between adjacent modules, while end-clamps are positioned at the ends of the array and typically offer stronger locking force.
3. Technical Characteristics of Mainstream PV Mounting Brands
Installers typically select partner brands based on roof type. The following are mainstream solutions in the market:
SnapNrack
A California-based company, its Ultra Rail Roof Mount System features a snap-in design for enhanced installation efficiency. It offers ground-mount solutions and pre-assembled systems, significantly reducing rooftop working time.
Unirac
Its product line covers residential and commercial scenarios, suitable for pitched roofs, flat roofs, and ground-mounted installations. Having participated in over 2.5 million projects, it boasts extensive application experience
IronRidge
Renowned for its structural strength, its pitched roof systems have been tested in extreme environments like Florida’s high-velocity hurricane zones. Operational since the 1990s, it holds technical advantages in wind load resistance and corrosion protection.
Quick Mount PV and EcoFasten
Focused on solutions for specialized roofs:
Standing Seam Metal Roofs: Utilize penetration-free clamping technology, attaching directly to the roof seams, eliminating leak risks and improving installation efficiency.
Clay/Spanish Tile Roofs: Developed tile replacement mounts that substitute existing roof tiles while integrating waterproofing, avoiding damage to brittle materials.
AllEarth Renewables
Specializes in ground-mounted tracking systems. Using dual-axis tracking technology, these systems enable modules to follow the sun’s path in real-time, increasing energy generation by 20-40% compared to fixed systems, making them suitable for projects with ample space and a focus on efficiency.
4. Key Considerations for Mounting System Selection
Roof Compatibility: The choice must correspond to the roof material (asphalt shingle/metal/clay tile, etc.), slope, and structural load capacity.
Waterproofing and Drainage Design: Penetrating installations must ensure a high waterproofing seal rating, while non-penetrating solutions require validation of clamping force and roof compatibility.
Cable Management: Integrated cable tray design impacts system tidiness and maintenance convenience.
Wind and Snow Loads: Must comply with local building codes and design requirements for wind and snow resistance.
Installation Efficiency: Modular design and ground pre-assembly capabilities significantly influence the construction timeline.
Conclusion
As the critical link connecting the power generation units to the building structure, the selection of the PV mounting system directly impacts the operational safety and performance output throughout the system’s 25-year lifecycle. It is recommended that owners prioritize installers with professional design capabilities and qualified partnerships with reputable brands, ensuring the perfect integration of the PV system with the building environment through customized mounting solutions.
(This article is compiled based on PV industry technical standards and manufacturer public data; specific solutions require determination after on-site inspection.)
Post time: Oct-31-2025