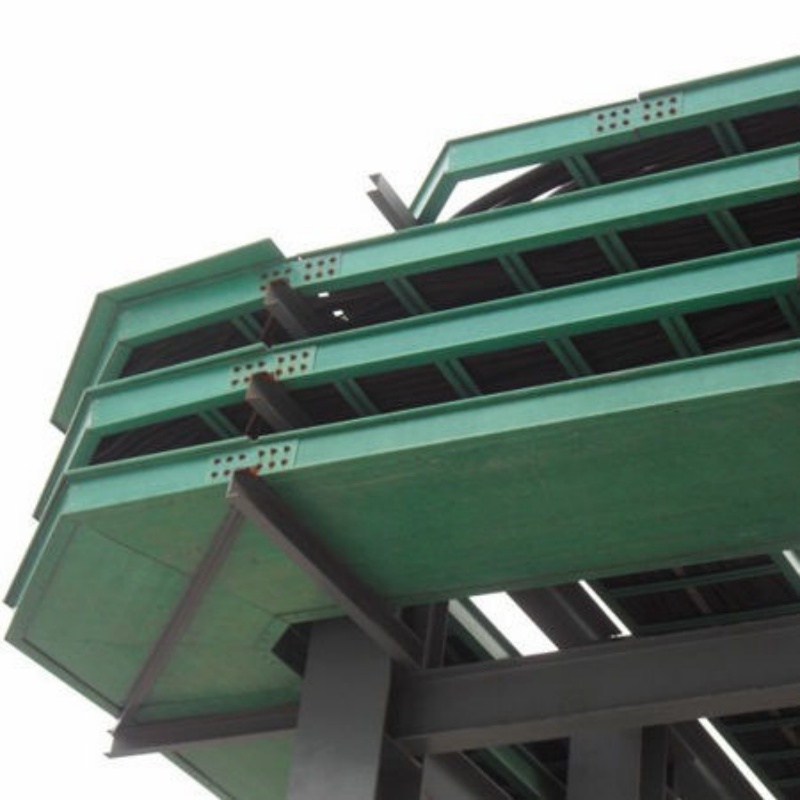
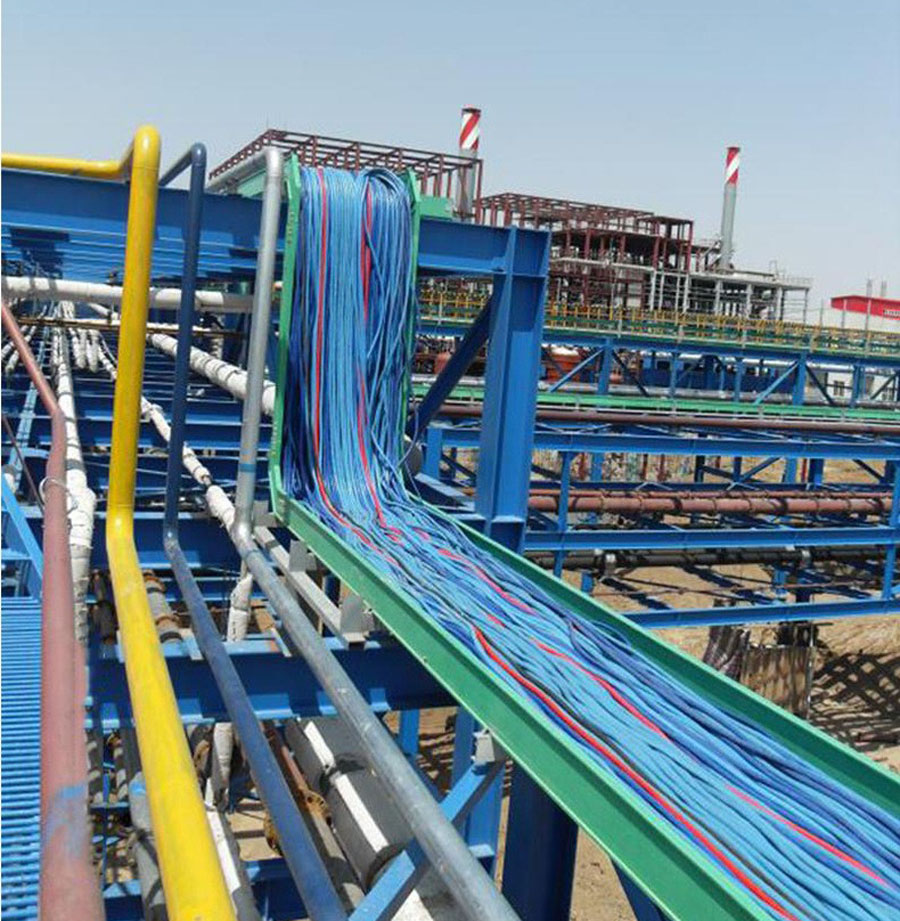
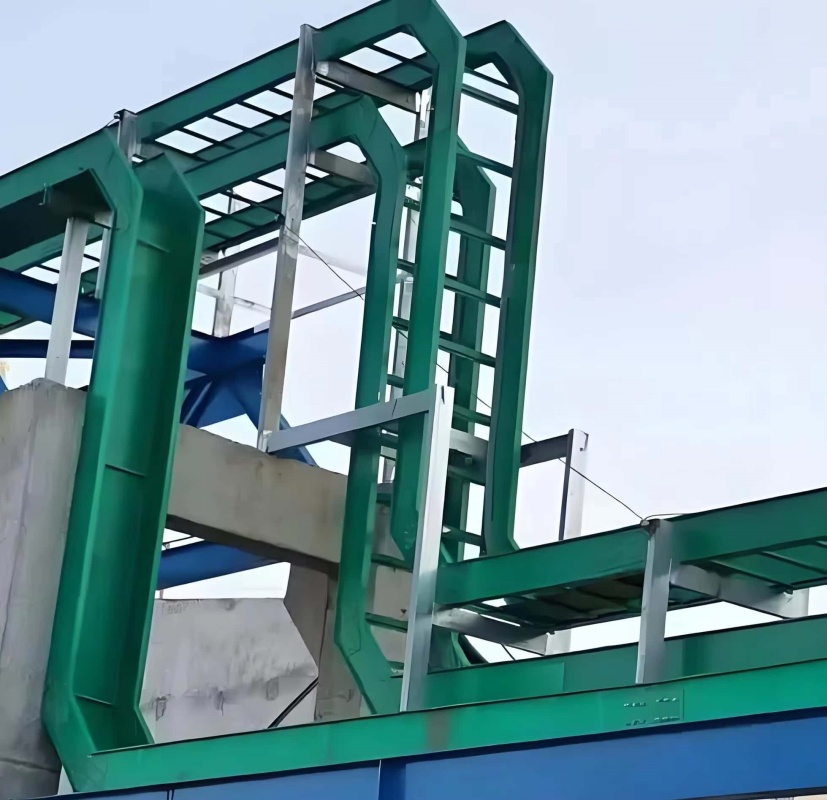
In the field of electrical installation, the selection of cable management systems is crucial for ensuring safety, efficiency, and durability. Among the many available materials, fiber-reinforced plastics (FRP) and glass fiber reinforced plastics (GRP) have garnered significant attention. Both materials can be used to manufacture cable trays and ladder racks, but their unique properties make them suitable for different applications. This article will explore the differences between FRP and GRP cable trays, highlighting their characteristics, advantages, and ideal application cases.
Understanding FRP and GRP
Before delving into the differences between the two, it is first necessary to understand what FRP and GRP are.
Fiber Reinforced Plastics (FRP)
Fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP) composites are composite materials with a polymer matrix and reinforced with fibers. These fibers can be made from a variety of materials, including glass fibers, carbon fibers, aramid fibers, or natural fibers. The most commonly used FRP in cable trays is glass fiber reinforced plastic (GRP). However, FRP can also contain other types of fibers, which can enhance certain properties such as strength, weight, and resistance to environmental factors.
Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (GRP)
Fiberglass reinforced plastic (GRP) is a special type of fiber-reinforced plastic (FRP) composite material, using glass fibers as reinforcement. It is renowned for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and durability. GRP is widely used in various fields such as construction, automotive, and electrical installations, and is particularly suitable for environments where the performance of traditional materials such as steel or aluminum is unsuitable.
Main differences between FRP and GRP cable trays
Although FRP and GRP are often used interchangeably, there are some key differences between them that affect the choice between FRP cable trays and GRP cable trays.
1. Composition
The main difference lies in their composition. FRP (fiber reinforced plastic) is a broader category encompassing various fibers, while GRP (glass fiber reinforced plastic) specifically refers to materials made using glass fibers. This distinction affects the mechanical properties and performance of cable trays.
2. Strength and Durability
Both FRP and GRP cable trays are known for their strength and durability. However, due to the properties of glass fiber, GRP cable trays generally have superior mechanical strength. This makes GRP the preferred choice for applications requiring high load-bearing capacity. On the other hand, FRP cable trays using other types of fibers may have different strength characteristics, which may be more advantageous in certain specific situations.
3. Corrosion Resistance
One of the most significant advantages of FRP and GRP cable trays is their corrosion resistance. However, GRP cable trays are particularly suitable for high humidity, chemical, or saltwater environments. The glass fibers in GRP have excellent corrosion resistance, resisting the erosion of a variety of corrosive substances, making them ideal for marine, chemical, and wastewater treatment applications. FRP cable trays also have some corrosion resistance, but their performance varies depending on the type of fiber used.
4. Weight
Fiber reinforced plastic (FRP) cable trays are generally lighter than fiberglass (GRP) cable trays. This is an advantage in applications where weight is critical, such as overhead applications or structures with weight restrictions. The weight reduction of FRP can also reduce transportation and installation costs. However, compared to GRP, the lightweight nature of FRP may come at the cost of some mechanical strength.
5. Thermal Properties
Thermal performance is another key difference between FRP and GRP. GRP cable trays typically offer better insulation, making them more suitable for environments with drastic temperature fluctuations. They can withstand higher temperatures without deformation or loss of structural integrity. FRP cable trays, on the other hand, may not perform as well as GRP in high-temperature applications, depending on the resin and fiber combination used.
6. Cost
Cost is always a factor to consider in any project. Generally speaking, FRP cable trays are more cost-effective than GRP cable trays. This is because FRP has lower raw material and manufacturing process costs. However, the initial cost advantage of FRP may be offset by potential long-term maintenance and replacement costs, especially in harsh environments where GRP may outperform FRP.
7. Aesthetic Considerations
In some applications, the aesthetics of cable trays are also an important factor. Fiberglass reinforced plastic (GRP) cable trays typically have a smoother surface and can be made in a variety of colors, making them more visually appealing in surface-mounted environments. Fiberglass reinforced plastic (FRP) cable trays, on the other hand, may lean more towards a utilitarian style and may not be suitable for all environments.
Applications of FRP and GRP Cable Trays
Understanding the differences between FRP and GRP cable trays can help in selecting the right product for a specific application.
FRP Cable Trays
FRP cable trays are ideal for:
- **Lightweight Applications:** In situations where weight is a critical factor, such as high-altitude installations.
– **Non-corrosive environment**: Suitable for indoor applications with minimal exposure to corrosive chemicals.
– **Cost-sensitive projects:** When budget constraints are the primary consideration, FRP can provide a more economical solution.
Fiberglass Cable Tray
Fiberglass cable trays are best suited for:
- **Harsh environments:** such as chemical plants, marine applications, and wastewater treatment facilities, where corrosion resistance is crucial.
– **Heavy-duty applications:** Situations requiring high mechanical strength to support heavy cables and equipment.
– **Temperature-sensitive installations:** In environments with extreme temperatures or large temperature fluctuations.
FRP and GRP cable trays each have their advantages, and the final choice depends on specific installation requirements. Understanding their differences in composition, strength, corrosion resistance, weight, thermal properties, cost, and aesthetics helps engineers and project managers make informed decisions. By selecting the appropriate cable management system, businesses can ensure the safety, efficiency, and lifespan of their electrical installations. Regardless of whether FRP or GRP is chosen, both materials represent significant advancements in cable management technology, providing reliable solutions for modern electrical infrastructure.
→ For all products,services and up to date information,please contact us.
Post time: Jan-07-2026