Solar panels have become a cornerstone of renewable energy, harnessing the sun’s energy to generate electricity. But what exactly is inside a solar panel that allows it to convert sunlight into usable energy? Understanding the components of a solar panel helps demystify the technology and highlights its importance in the fight against climate change.
At the heart of a solar panel are photovoltaic (PV) cells, which are typically made of silicon. Silicon is a semiconductor material that absorbs sunlight and converts it into electricity. These cells are arranged in a grid pattern and are the main function of a solar panel. When sunlight hits a PV cell, it excites electrons, creating an electric current. This process is called the photovoltaic effect.
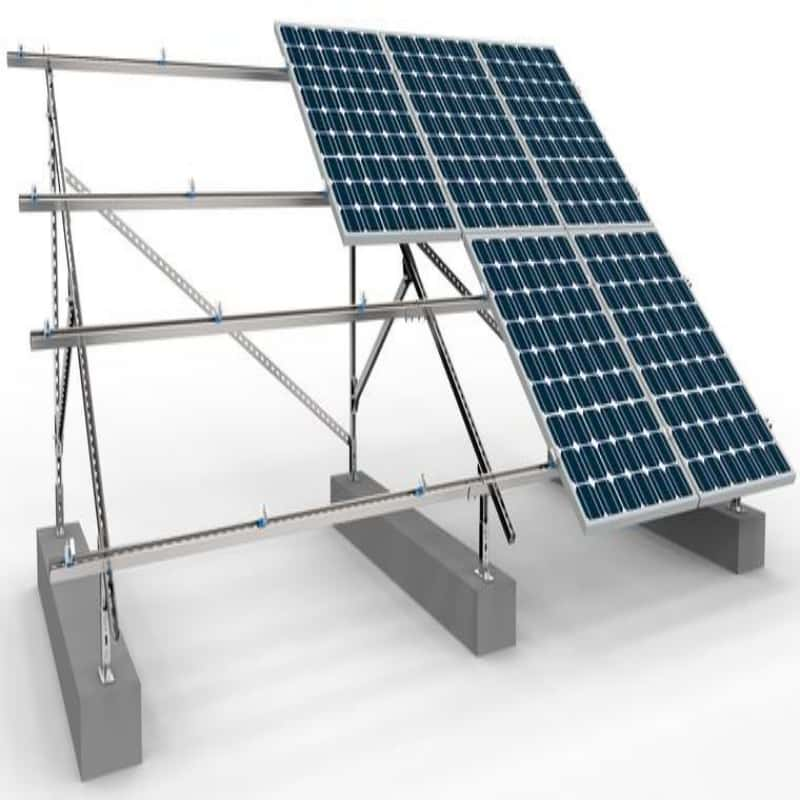
In addition to the photovoltaic cells, solar panels contain several other important components. The backsheet is usually made of a durable polymer and provides insulation and protection for the cells. The frontsheet is usually made of tempered glass, protecting the cells from environmental elements while allowing sunlight to pass through. The glass is often coated with an anti-reflective coating to maximize light absorption.
Solar panels also contain a junction box that houses the electrical connections and delivers the generated electricity to the inverter. The inverter is crucial because it converts the direct current (DC) generated by the solar panels into alternating current (AC), the form of electricity used by homes and businesses.
The frame of a solar panel is typically made of aluminum, which provides structural support and facilitates installation. These components work together to capture sunlight and convert it into clean, renewable energy, making solar panels an essential component of sustainable energy solutions. Understanding the makeup of a solar panel not only highlights its complexity, but also reveals its potential to change our energy landscape.
→ For all products,services and up to date information,please contact us.
Post time: Apr-23-2025